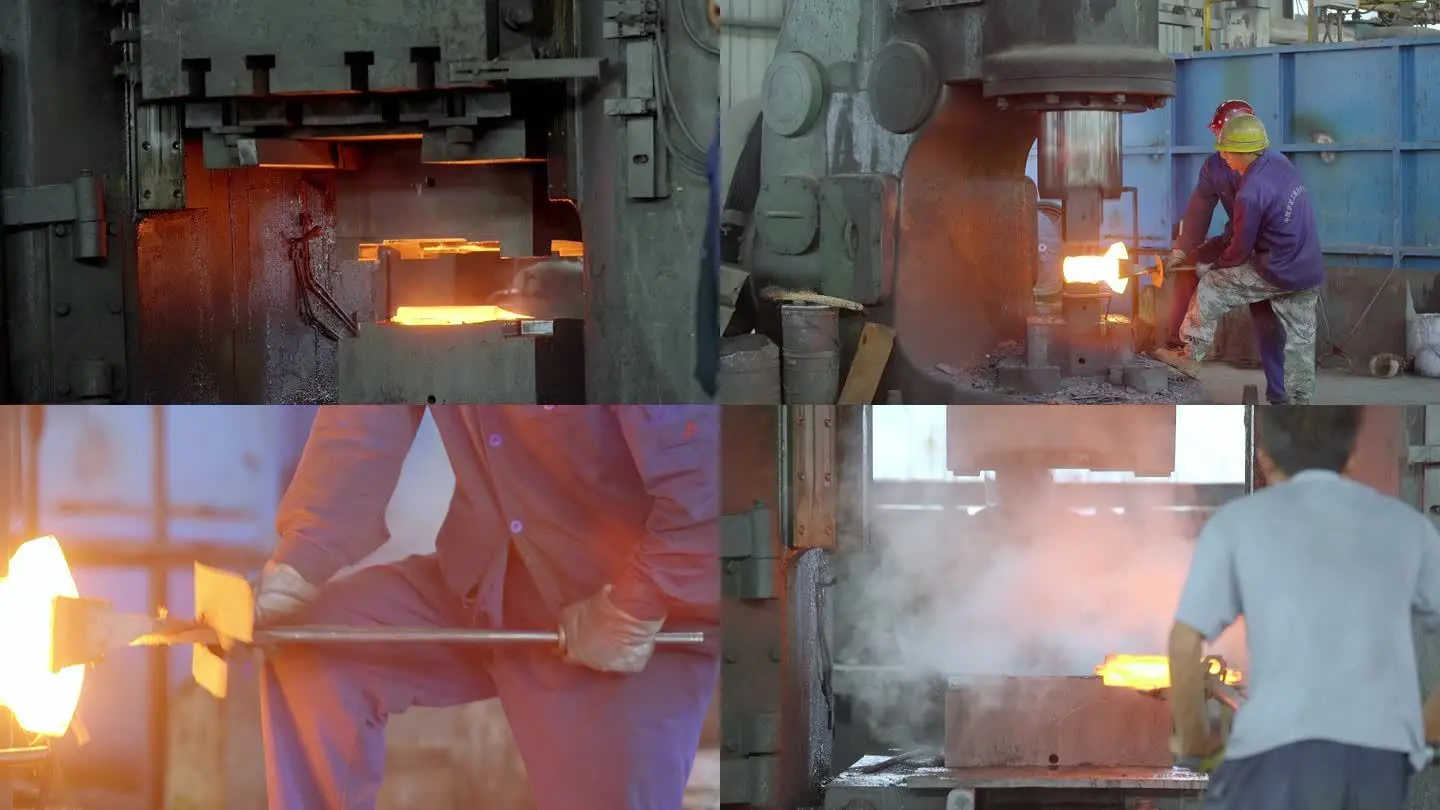
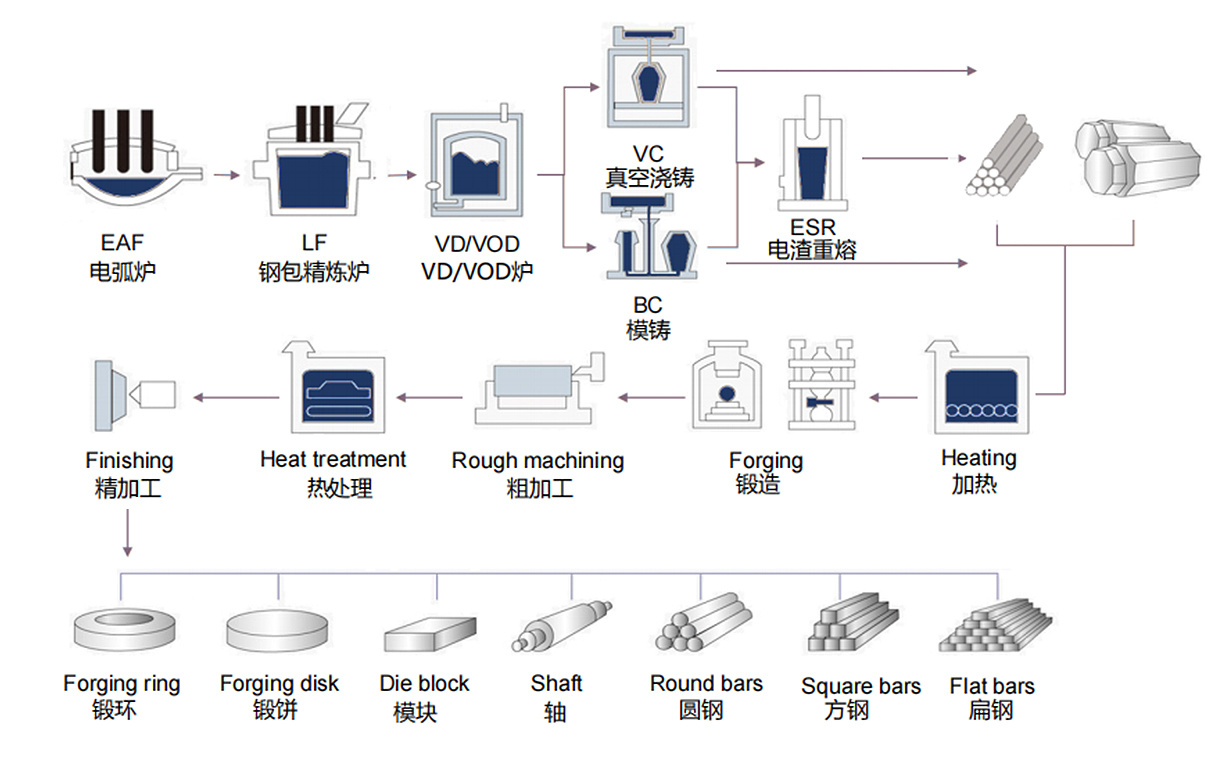
Forging
Forging is a processing method that uses forging machinery to apply pressure to metal blanks to produce plastic deformation to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, certain shapes and sizes, and is one of the two major components of forging (forging and stamping). Through forging, the defects such as loose casting state generated by the metal in the smelting process can be eliminated, the microstructure structure can be optimized, and the mechanical properties of forgings are generally better than castings of the same material due to the preservation of complete metal streamlines.
The initial recrystallization temperature of steel is about 727 °C, but 800 °C is generally used as the dividing line, and hot forging is higher than 800 °C; Between 300~800 °C is called warm forging or semi-hot forging, and forging at room temperature is called cold forging. Forgings used in most industries are hot forging, warm forging and cold forging are mainly used for forging parts such as automobiles and general machinery, and warm forging and cold forging can effectively save materials.
According to the forming mechanism, forging can be divided into open forging, die forging, ring grinding, and special forging.
The forging materials are mainly carbon steel and alloy steel of various compositions, followed by aluminum, magnesium, copper, titanium, etc. and their alloys. The raw state of the material is bar, ingot, metal powder and liquid metal.
Compared with castings, the microstructure and mechanical properties of metals can be improved after forging. After the casting structure is deformed by hot processing by the forging method, due to the deformation and recrystallization of the metal, the original coarse dendrite and columnar grains become the equiaxed recrystallization structure with finer grains and uniform size, so that the original segregation, looseness, porosity, slag inclusion and other compaction and welding in the steel ingot, its structure becomes more compact, and the plasticity and mechanical properties of the metal are improved.
The mechanical properties of castings are lower than those of forgings of the same material. In addition, forging can ensure the continuity of the metal fiber structure, make the fiber structure of the forging consistent with the shape of the forging, and the metal streamline is complete, which can ensure that the parts have good mechanical properties and long service life, and the forgings produced by precision die forging, cold extrusion, warm extrusion and other processes are incomparable to castings.
Our Forged Parts are manufactured using advanced forging techniques to ensure superior strength, durability, and precision. Ideal for automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery applications, our forged parts are available in various materials, including steel, aluminum, and titanium.Contact us today for more information and a customized quote.