Graphite dual-use items exported to the United States will be subject to stricter scrutiny!
On December 3, 2024, the Ministry of Commerce decided to strengthen the export control of relevant dual-use items to the United States, and this announcement will be officially implemented from the date of publication.
The relevant matters are announced as follows:
1. The export of dual-use items to military users or for military purposes in the United States is prohibited.
2. In principle, the export of gallium, germanium, antimony, and related dual-use items to the United States will not be permitted; for graphite dual-use items exported to the United States, stricter end-user and end-use reviews will be implemented.
The announcement emphasizes that any organization or individual from any country or region that violates the above regulations by transferring or providing relevant dual-use items originating from the People's Republic of China to organizations or individuals in the United States will be held legally accountable.
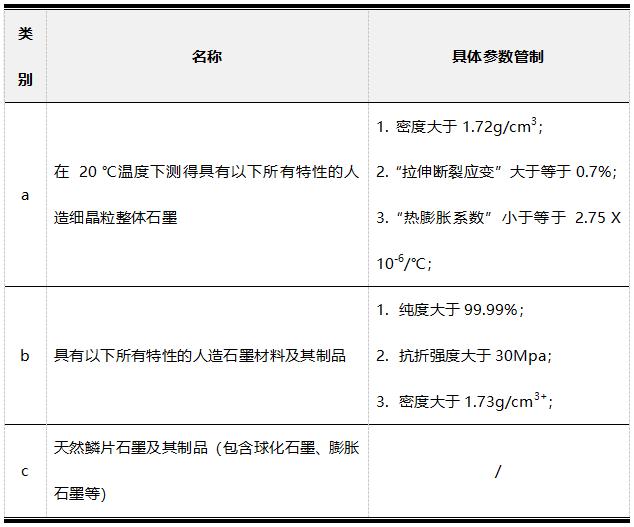
According to the newly released "Export Control List of Dual-Use Items of the People's Republic of China" on November 5, item 1C108 graphite and its products are explicitly controlled.
表:1C108石墨及其制品管制项目
The "game" of graphite between China and the United States began with export controls on graphite in 2023, which will continue and escalate in 2024. The reasons behind this cannot be casually speculated upon; however, this announcement signifies that high-end graphite materials and products have ascended to a national strategic level, carrying certain political attributes. In the future, the value of these strategic minerals will continue to manifest and even amplify.
Moreover, it should not be forgotten that on September 27, 2024, the 301 tariffs imposed by the United States on China will officially take effect. Graphite, however, is an "exception." The high tariffs imposed by the United States on China aim to protect domestic industries and reduce dependence on Chinese products. Nevertheless, the United States has shown considerable caution in handling this critical mineral, postponing the tariff imposition date to 2026. This decision may superficially appear as leniency towards Chinese graphite, but it actually reveals the United States' high dependence on China in this field and its extreme self-serving behavior.
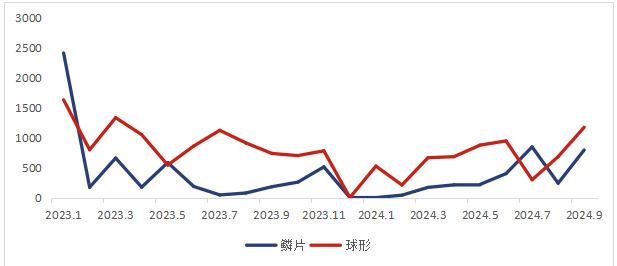
Following the announcement of export controls in 2023, data indicates that the export of natural graphite products has been somewhat affected. Taking the export situation of flake and spherical graphite to the United States as an example, the export conditions before and after the implementation of the controls are as follows:
Export situation of flake and spherical graphite to the United States from 2023 to September 2024 (tons)
The important connotation of "export control"
Export control is a set of laws and regulations established by a country for the export of goods, driven by political, economic, military, and foreign policy needs, which involves controlling the countries of export and the exported goods. The main measures include: (1) implementing an export licensing system for raw materials, semi-finished products, and goods in short supply required for domestic production, with limited exports; (2) implementing special export licenses for strategic materials, cutting-edge technologies, and advanced products, with strict control; (3) automatically restricting exports of certain goods to fulfill international obligations; (4) regulating the quality and price of exported goods to enhance their competitiveness.
The necessity of graphite export control
On October 20, 2023, the Ministry of Commerce and the General Administration of Customs jointly issued a notice on the export control of graphite items, and the continuation of this control policy in 2024 indicates its necessity and correctness, reflecting that the new international economic and policy situation still has a profound impact on the graphite industry. According to the editor of Powder Network, as the world's largest producer and exporter of graphite, the sustainability, safety, and stability of graphite resources and industry are of utmost importance for China. In the long run, this policy is more protective than restrictive. Sun Qing, honorary president of the China Carbon Industry Association, believes that the recent adjustment of control measures by the Ministry of Commerce is entirely due to the reasons for industry development, with no other considerations.
Taking high-purity natural graphite as an example, it is widely used in advanced refractory materials and coatings in the metallurgical industry, stabilizers for military pyrotechnic materials, pencil leads in the light industry, carbon brushes in the electrical industry, electrodes in the battery industry, and catalysts in the fertilizer industry. Flake graphite, after deep processing, can produce graphite slurries, graphite sealing materials, composite materials, graphite products, and graphite friction-reducing additives, becoming an important non-metallic mineral raw material for various industrial sectors. Taking special graphite as an example, the current rapid development of industries such as semiconductors, lithium batteries, photovoltaic solar energy, synthetic diamonds, electrical discharge machining, and nuclear power in China is expected to intensify trade competition for high-end graphite materials in the future, with market demand also showing rapid growth, which will play an important supporting role in national security and economic development. Strategic resources in the great power game represent discourse power, which must be firmly in our hands.